Due to the decreasing incidence of the new coronavirus infections in Germany, the federal and state governments have agreed on a step-by-step plan to relax restrictive measures in force. After a meeting on Wednesday between Chancellor Olaf Scholz and the premiers of the Laender, a three-step plan with the removal of the vast majority of restrictions which should bring Germany back to much more normality by 20 March was agreed. This is because the current Infection Protection Act only allows these protective measures against Corona until 19 March.
Here’s what you need to know.
——-
First step from 17 February:
The first opening steps affect retail shops and private gatherings:
- Access to retail shops nationwide for all persons without controls. However, mandatory nose-mouth masks still apply, FFP2 masks recommended, insofar as it is not prescribed by state law
- Private meetings for vaccinated and recovered persons without limitation of the number of participants allowed. And for unvaccinated persons, the current restrictions (one person from a household and a maximum of two persons from another household) remain in place until 19 March
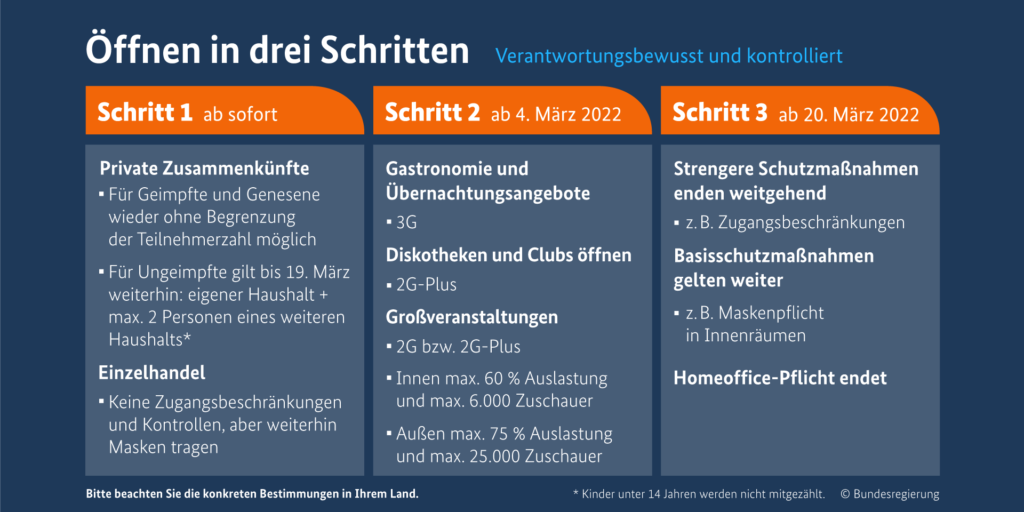
Second step, starting on 4 March:
- 3G regulations (vaccinated, recovered and persons with a daily test) for the catering industry and in hotels. Until now, the 2G-plus rule (recovered persons and vaccinated persons with a daily test or with a third vaccination) was in effect
- Discotheques and clubs may reopen with the 2G-plus rule (recovered persons and vaccinated persons with a daily test or with a third vaccination).
- At major events (including sports), people who have recovered and have been vaccinated (2G regulation) or people who have recovered and been vaccinated with a daily test or third vaccination (2G Plus regulation) can participate as spectators.
- For indoor events, a maximum capacity utilisation of 60 per cent of the respective maximum capacity is permitted, whereby the number of spectators may not exceed 6,000.
- For outdoor events, a maximum capacity utilisation of 75 per cent of the respective maximum capacity is permitted, whereby the number of spectators may not exceed 25,000.
Third step from 20 March:
- “All protective measures are dropped”. Mandatory home office rule ends.
Employers may, however, continue to offer home office work in agreement with employees if there are no operational reasons to the contrary and it is in the interest of occupational infection control (e.g. when working in open-plan offices).
In the view of the Federal Governments and the states, a low-threshold basic protection measures are still necessary beyond 19 March 2022 to contain the incidence of infection and to protect at-risk groups. These include, in particular, the obligation to wear a mask in enclosed public facilities as well as in buses and trains, and maintain the social distance and general hygiene requirements.
The concrete implementation of the resolutions is up to the federal states. In addition, the states will decide on their own responsibility about opening steps in those areas that have little or no supra-regional impact in view of the different levels of infection and vaccination rates as well as the burdens on the health system.
Federal Chancellor Scholz and the heads of state governments will meet again on 17 March 2022 or earlier if the situation makes it necessary.
Femi Awoniyi
 THE AFRICAN COURIER. Reporting Africa and its Diaspora! The African Courier is an international magazine published in Germany to report on Africa and the Diaspora African experience. The first issue of the bimonthly magazine appeared on the newsstands on 15 February 1998. The African Courier is a communication forum for European-African political, economic and cultural exchanges, and a voice for Africa in Europe.
THE AFRICAN COURIER. Reporting Africa and its Diaspora! The African Courier is an international magazine published in Germany to report on Africa and the Diaspora African experience. The first issue of the bimonthly magazine appeared on the newsstands on 15 February 1998. The African Courier is a communication forum for European-African political, economic and cultural exchanges, and a voice for Africa in Europe.






























